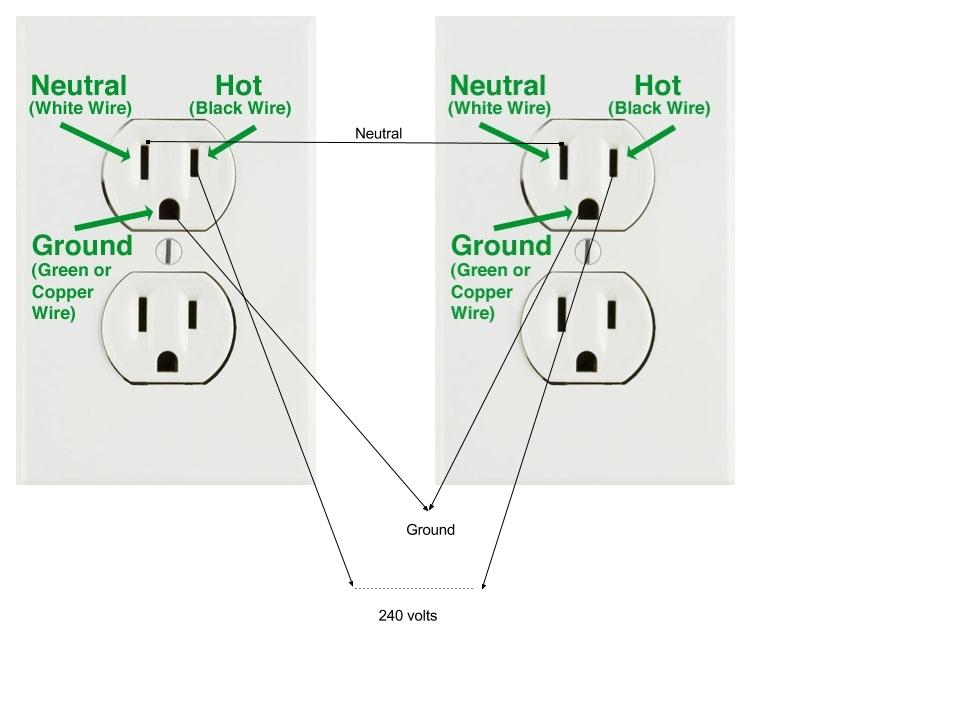
Exemplary Tips About Can I Use 240V In 120V
Is 220 And 240 Volt The Same
Understanding Voltage Differences
1. Why Voltage Matters
Ever wondered why some electrical outlets look different, or why certain appliances require specific plugs? The answer often boils down to voltage. Think of voltage like the water pressure in your home's pipes. If the pressure is too low, you might not get a good shower. Too high, and you risk bursting a pipe. Electricity works similarly. 120V is common in North America for smaller appliances, while 240V is used for things that need more power, like ovens and dryers.
Using the wrong voltage can lead to problems. Imagine trying to power a high-powered appliance with a low-voltage supply — it simply won't work properly, and you might damage the appliance. Conversely, plugging a device designed for lower voltage into a high-voltage outlet is a recipe for disaster — sparks, smoke, and potential fire are all real possibilities. It's not a fun situation!
The key takeaway? Always check the voltage requirements of your appliances and the voltage supplied by your outlets before plugging anything in. This information is usually printed on the appliance itself or in its user manual. A little bit of due diligence can save you a lot of headaches (and potentially your home!).
Think of your electronics like picky eaters. Some only want small portions (120V), while others need a hearty meal (240V). Giving them the wrong thing can lead to indigestion, or in this case, a fried circuit board. So, let's dive into whether you can ever get away with substituting one for the other.

The Golden Question
2. The Short Answer
Alright, let's cut to the chase: No, you absolutely cannot directly use a 240V appliance in a 120V outlet, and vice versa. Trying to do so is like trying to fit a square peg in a round hole — it's simply not going to work, and you're likely to cause some serious damage.
Why is this the case? Because appliances are designed to operate within a specific voltage range. They have internal components and circuits that are calibrated to work efficiently and safely at that voltage. When you supply the wrong voltage, you're essentially throwing off this delicate balance.
Using a 240V appliance on a 120V circuit won't necessarily cause an immediate explosion (although, depending on the appliance, it could). More likely, the appliance simply won't work. It might hum weakly, or maybe nothing will happen at all. The lack of sufficient voltage means the appliance can't draw the power it needs to function.
However, constantly trying to use an appliance on the wrong voltage could eventually damage its internal components. This can lead to costly repairs or even require you to replace the entire appliance. Save yourself the trouble and always match the voltage!
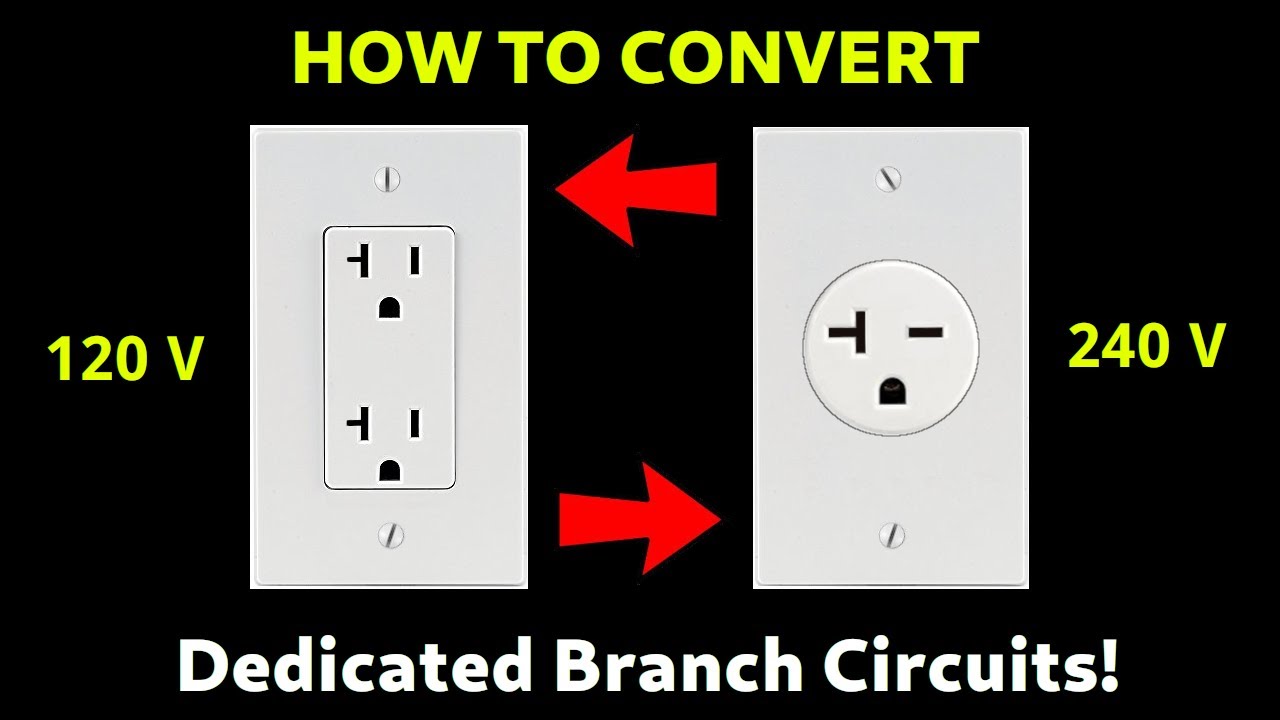
What Happens if You Try It Anyway? (Spoiler Alert
3. The Potential Consequences
Okay, so we've established that you shouldn't try to use a 240V appliance in a 120V outlet. But what are the actual risks involved? Let's break it down.
At best, the appliance just won't work. It might sit there silently, mocking your attempt to defy electrical principles. At worst, you could cause serious damage to the appliance, the outlet, or even your home's electrical system.
Imagine plugging a powerful hairdryer designed for 240V into a 120V outlet. The hairdryer needs twice the voltage to heat up properly. When you provide only half the juice, the motor might struggle and overheat, potentially causing it to burn out. Or, in more extreme cases, it could create a short circuit that trips the breaker or even starts a fire.
It's also worth noting that repeatedly attempting to use an appliance on the wrong voltage can weaken its internal components over time, even if you don't see immediate damage. This can lead to premature failure and the need for expensive repairs. So, think of your appliances as delicate little machines that need the right fuel to run smoothly. Don't starve them!
Voltage Converters and Transformers
4. A Solution, But with Caveats
Now, before you resign yourself to a life of never using your favorite 240V appliance in your 120V home, there is a potential workaround: voltage converters and transformers. These devices can step up or step down the voltage, allowing you to use appliances designed for different voltages.
A voltage converter is generally used for small electronic devices like phones, laptops, and cameras. It essentially changes the voltage to match the device's requirements. A transformer, on the other hand, is typically used for larger appliances that consume more power, such as kitchen appliances or power tools.
However, it's crucial to choose the right type of converter or transformer for your specific appliance. Using the wrong one can be just as dangerous as plugging the appliance directly into the wrong outlet. You need to ensure that the converter or transformer can handle the appliance's power requirements (measured in watts) and that it's designed for continuous use if you plan to use the appliance for extended periods.
Also, be aware that voltage converters and transformers can be expensive. Depending on the size and power rating, they can cost anywhere from a few dollars to several hundred dollars. In some cases, it might be more cost-effective to simply purchase a new appliance designed for your local voltage.

MACARLON Level 1 & 2 EV Charger, 110V240V 16A Portable
Adapters vs. Converters
5. Don't Get Them Confused!
It's easy to confuse adapters and converters, but they serve different purposes. An adapter simply changes the shape of the plug so it can fit into a different type of outlet. It does not change the voltage. So, if you're traveling from a country with 240V outlets to a country with 120V outlets, an adapter alone won't do the trick. You'll still need a voltage converter.
Think of an adapter as a translator. It helps you understand the language of the outlet by changing the shape of your plug. But it doesn't change the underlying meaning (the voltage). A converter, on the other hand, actually rewrites the message to make it compatible with the new language.
Before using any adapter or converter, carefully check the voltage requirements of your appliance and the voltage supplied by the outlet. Look for labels on the appliance that indicate its voltage range. If the voltage is different, you'll need a converter. If the voltage is the same, but the plug shape is different, you'll need an adapter.
Remember, using the wrong adapter or converter can be dangerous. It's always better to be safe than sorry. If you're unsure, consult a qualified electrician or refer to the appliance's user manual.