Brilliant Strategies Of Info About Do I Need Single-phase Or 3 Phase

Understanding Your Power Needs
1. What's the Fuss About Phases?
Ever wondered why some buildings hum with a different kind of electrical energy than others? It often comes down to the type of electrical service: single-phase or three-phase. Think of it like this: single-phase is like a solo guitarist, while three-phase is a full band. Both can make music (or power your devices), but they do it in different ways and with varying levels of oomph.
The key difference lies in how the power is delivered. Single-phase power is what you typically find in homes and smaller businesses. It's simpler and cheaper to install, making it perfect for powering everyday appliances like your fridge, TV, and that essential coffee maker. But when you need to run heavy-duty equipment, single-phase might start to sweat.
Three-phase power, on the other hand, is the powerhouse of the electrical world. It provides a smoother, more consistent flow of electricity, making it ideal for industrial machinery, large air conditioning systems, and other high-demand applications. Imagine trying to run a factory on the same power you use to toast your bread — it wouldn't be pretty!
So, how do you know which one you need? Well, that's the million-dollar question, and we're here to help you answer it. Let's delve deeper, shall we?

Decoding Single-Phase Power
2. Why Single-Phase is So Common in Residences
Single-phase power is the undisputed champion of residential electricity. It's simple, reliable, and generally sufficient for the needs of a typical household. You probably don't need a massive industrial motor to power your blender (unless you're making some seriously hardcore smoothies).
The beauty of single-phase lies in its ease of use and affordability. Wiring is straightforward, and the equipment required is relatively inexpensive. Plus, utility companies often offer lower rates for single-phase service, making it a budget-friendly option for homeowners.
Think about all the appliances in your home: lights, computers, washing machines, dryers, and maybe even a small window AC unit. All of these things run perfectly well on single-phase power. It's like having a dependable friend who's always there to keep the lights on (literally!).
However, there are limitations. If you're planning a major renovation that involves adding a workshop with heavy-duty power tools, or you're thinking about installing a whole-house electric vehicle charger, you might need to consider whether single-phase can handle the increased load. Overloading your single-phase system can lead to tripped breakers and potential electrical hazards, which is definitely something we want to avoid.
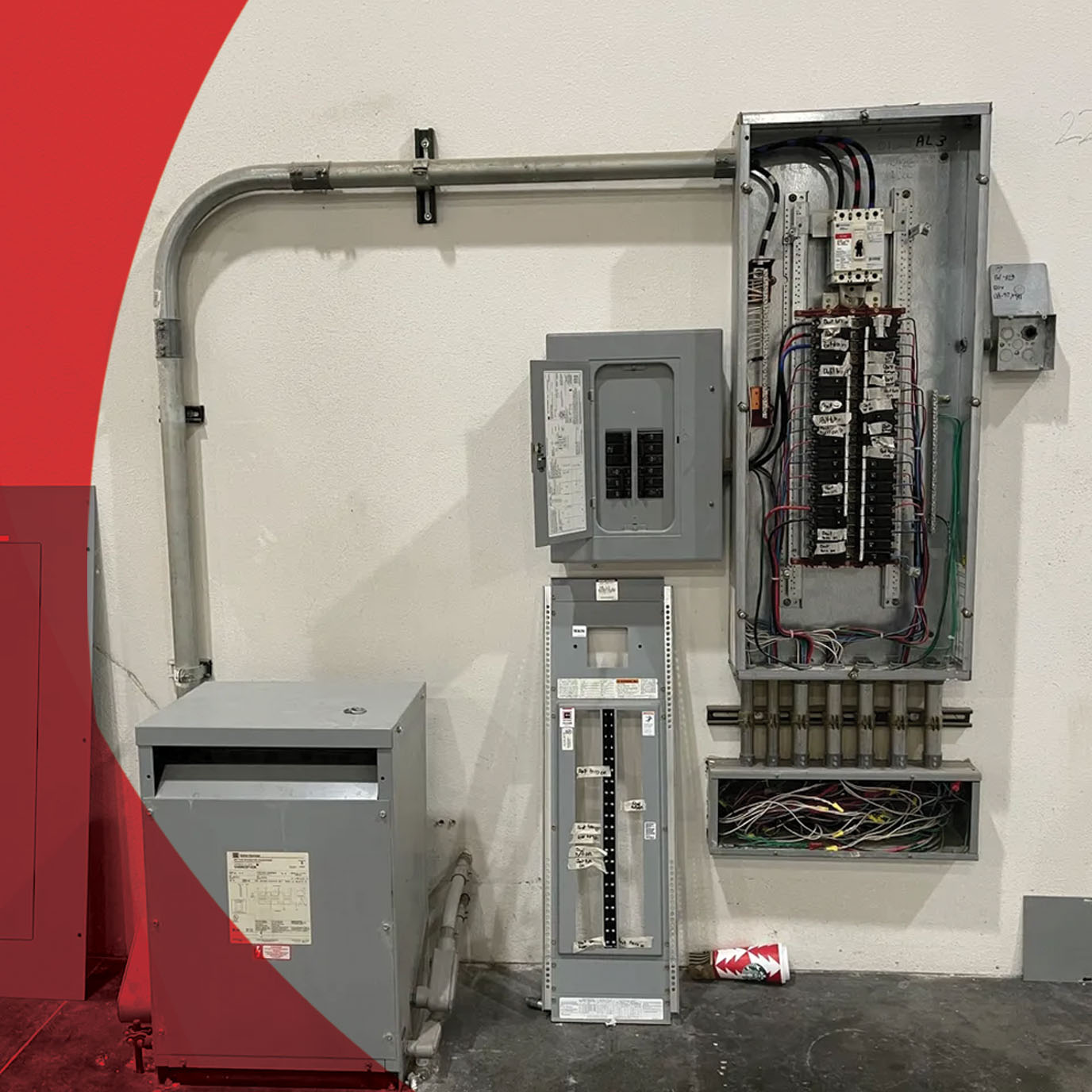
Unleashing Three-Phase Power
3. Where Three-Phase Thrives
Now, let's talk about the big leagues: three-phase power. This is the electricity of factories, warehouses, hospitals, and any other facility with substantial power demands. It's the strong, silent type that keeps everything running smoothly behind the scenes.
The main advantage of three-phase power is its ability to deliver a larger amount of power more efficiently. This is because it uses three separate alternating currents that are offset from each other, creating a constant and smooth flow of electricity. Imagine three friends pushing a car together, instead of one person struggling alone — that's essentially how three-phase works.
Large motors, industrial machinery, and high-capacity HVAC systems all benefit from the consistent power provided by three-phase. It reduces stress on equipment, extends lifespan, and improves overall performance. Think of it as giving your machinery a constant energy boost, allowing it to work harder and longer.
But three-phase power isn't just about raw power; it's also about efficiency. Because the load is distributed across three phases, the current is lower, which reduces heat loss and improves energy efficiency. This can translate into significant cost savings for businesses with high power consumption. However, for most homes, the expense and complexity of installing three-phase far outweigh the benefits.
Assessing Your Power Needs
4. Making the Right Choice for Your Situation
So, how do you determine whether you need single-phase or three-phase power? Start by evaluating your current and future electrical needs. Consider the types of appliances and equipment you'll be using, their power requirements, and how often you'll be using them simultaneously. Are you just running a few lights and a TV, or are you powering a welding shop?
If you're unsure about your power requirements, consult with a qualified electrician. They can conduct a load calculation to determine the total amount of power you'll need and recommend the appropriate electrical service. This is particularly important if you're planning a major renovation or adding new equipment that will significantly increase your power consumption.
Another factor to consider is the cost of installation. Three-phase power typically requires more complex wiring and specialized equipment, which can significantly increase the installation cost. However, if you have high power demands, the long-term cost savings from improved efficiency may outweigh the initial investment.
Ultimately, the decision of whether to go with single-phase or three-phase power depends on your specific needs and circumstances. There's no one-size-fits-all answer, but by carefully assessing your power requirements and consulting with a qualified electrician, you can make the right choice for your home or business.

Upgrading to Three-Phase
5. Weighing the Pros and Cons
Let's say you've determined that your power needs exceed the capabilities of single-phase. Should you upgrade to three-phase? The answer is, "it depends." While three-phase offers numerous advantages, it also comes with its own set of challenges and costs. It's a bit like deciding whether to buy a sports car or a minivan — both have their strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on your individual needs.
The primary advantage of upgrading to three-phase is the ability to handle significantly higher power loads. This is particularly beneficial for businesses that rely on heavy machinery, industrial equipment, or large HVAC systems. Three-phase power can also improve the efficiency and reliability of these systems, leading to cost savings in the long run.
However, upgrading to three-phase can be a significant investment. It typically involves running new service lines from the utility company, installing a new electrical panel, and upgrading wiring throughout your building. The cost can vary depending on the complexity of the installation and local regulations.
Before making the decision to upgrade, get multiple quotes from qualified electricians and carefully weigh the costs against the potential benefits. Consider your long-term power needs and whether the improved efficiency and reliability of three-phase will justify the investment. Sometimes, alternative solutions, such as upgrading your single-phase panel or implementing energy-saving measures, may be more cost-effective.

FAQs About Single-Phase and Three-Phase Power
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Here are some common questions people have about single-phase and three-phase power:
Q: How can I tell if my home has single-phase or three-phase power?
A: Check your electrical panel. Most homes have a single main breaker. If you see multiple main breakers labeled "A," "B," and "C," you likely have three-phase power. However, the easiest way is to contact your utility company or a qualified electrician.
Q: Can I convert single-phase to three-phase?
A: Yes, it's possible using a device called a rotary phase converter or a static phase converter. However, these converters have limitations and may not be suitable for all applications. Consult with an electrician to determine the best solution for your needs.
Q: Is three-phase power more dangerous than single-phase?
A: Not necessarily. Both single-phase and three-phase power can be dangerous if not handled properly. Always follow safety precautions and hire a qualified electrician for any electrical work.
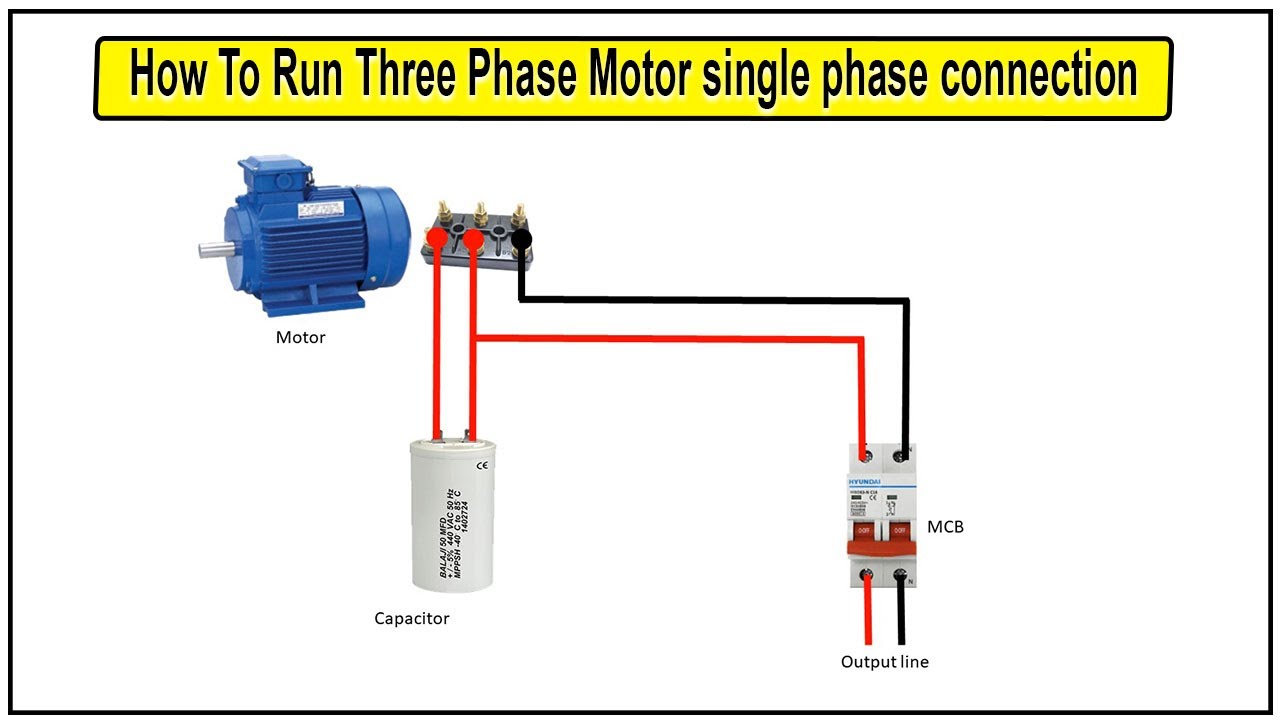
Q: What happens if I try to run a three-phase motor on single-phase power?
A: It won't work! Three-phase motors require three-phase power to operate properly. You'll need a phase converter or a different motor designed for single-phase operation.